A) Reagent block, where water is treated with chemical reagent (coagulum and flocculant)
B) Thin-layer clarification tank — where water is decontaminated by the action of gravity
This is the way of physical and chemical treatment on this equipment, which ensures separation of both solid and suspended particles and dissolved impurities.
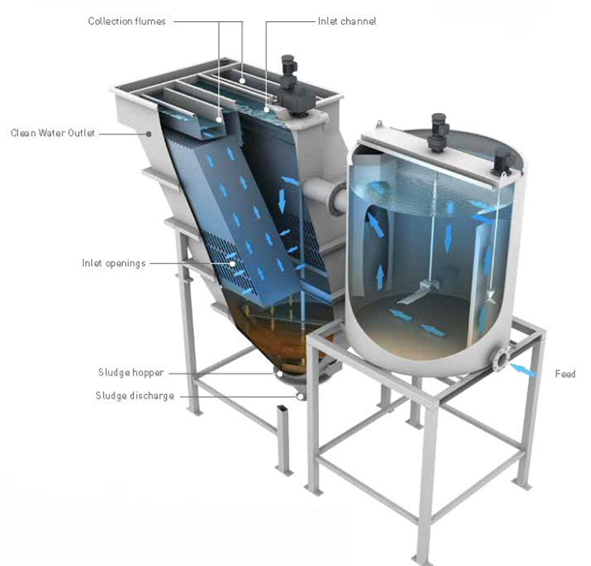

Reagent unit
This unit consists of two zones:
Coagulation unit, which has a high-speed mixer and is required for maximum distribution of the coagulum in the volume of feed water;
Flocculation unit, which has slow mixer and is designed for aggregation of the formed participles.
Process description
Coagulation – is the process of sticking of colloidal particles into larger aggregates, resulting from their collision during Brownian motion or mixing with the addition of the coagulant. At this time coagulum precipitates.
Coagulants (these are usually soluble salts of iron and aluminium) intensify coagulation process. After adding these substances into the water, a new low soluble phase is formed (as a result of hydrolysis – water-substance interaction). Thus, the process of coagulation is progressive aggregation of participles and decrease of their number in the volume of dispersion medium.
