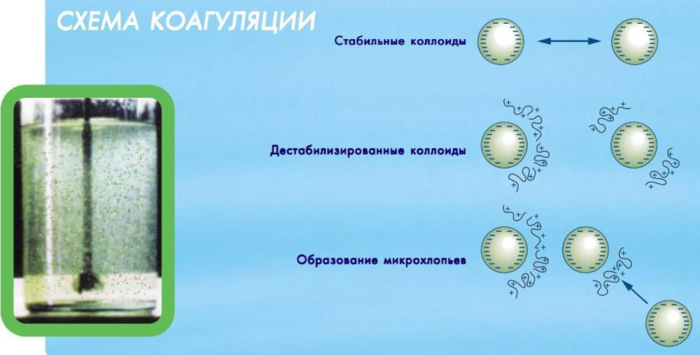
Flocculation (Latin floccule – shreds, flakes) – formation of loose flocculent quickly precipitating aggregates (floccules) from the small participles of dispersion phase, that are suspended in a liquid medium using flocculants.
Flocculants are water-soluble linear polymers consisting of a large number of groups. In the wastewater technology, flocculants are usually used in addition to coagulants, as they expand optimal areas of coagulation (by pH and by temperature), densify and strengthen formed floccules, reduce coagulant consumption, increase the reliability of work and productiveness of the water treatment equipment.
Adding flocculants to the feed water increases the speed of formation and subsequent precipitation of the flakes formed during the coagulation process. At the same time sediment density increases, and the effect of coagulant substances becomes more effective.

Thin-layer clarification tank
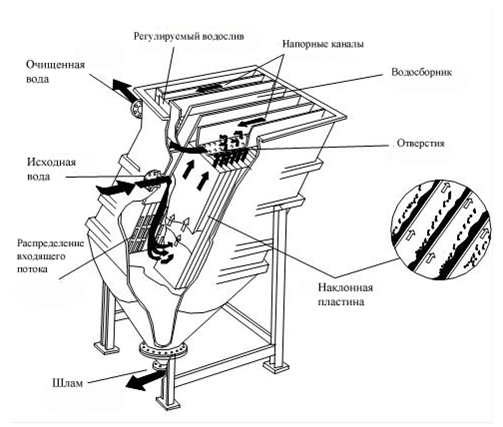
To increase the efficiency of sludging, thin-layer clarification tanks are used. At the shallow depth, sludging proceeds quickly, it allows to reduce the size of clarification tank. The use of thin-layer elements can significantly shorten the duration of sludging and consequently reduce the volume of clarification tanks. Thin-layer clarification tanks can significantly intensify the process of sedimentation, reduce the area of building by 60% and increase the effect of water clarification by 25-30% in comparison with commonly used clarification tanks.
Like common clarification tanks, they have a water-distributing system, sludging zone, water collection zone, and sediment collection zone. Feed water through the nozzle enters the water distribution system and the flow goes to the bottom part of the clarification unit for the purification. Water clarification occurs when the flow goes upward through the thin-layer plate. When the flow containing floccules moves upward, floccules sediment and flow by the inclined plates into the bottom part of the clarification tank – sedimentation zone (sludge tank), where sludge is condensed and discharged through the sludge disposal pipe. Clarified water goes through the inclined plates, and discharges on the top through special openings (water collection zone), and then through the clarification tank and the regulated drain enters the container of clarified water.
Clarification tank construction provides the uniform flow of the clarified water under the drop of pressure, and ensures the use of the whole surface of the clarification tank. This increases reliability, reduces the effect on the liquid fluidity, and inhibit sediment formation.
